The Role and Importance of Burettes in Laboratory Work


The word ‘burette’ has French origins – coined by the chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac.
Sensitivity and accuracy are two critical components, especially for laboratory test measurements and analyses. Without these components, it is impossible to derive reliable results related to the procedures performed. There are specific laboratory instruments that help ensure the accuracy and precision of certain measurements. One of these instruments is known as a burette.
A burette is a laboratory instrument with high accuracy used in the process of titration which consists of a long, graduated glass tube, with a stopcock on its lower end.
The choice of burette depends on the requirements of the experiment, including the level of accuracy needed, the volume of liquid to be dispensed, and the chemical nature of the solutions involved. Here's an overview of the main types of burettes:
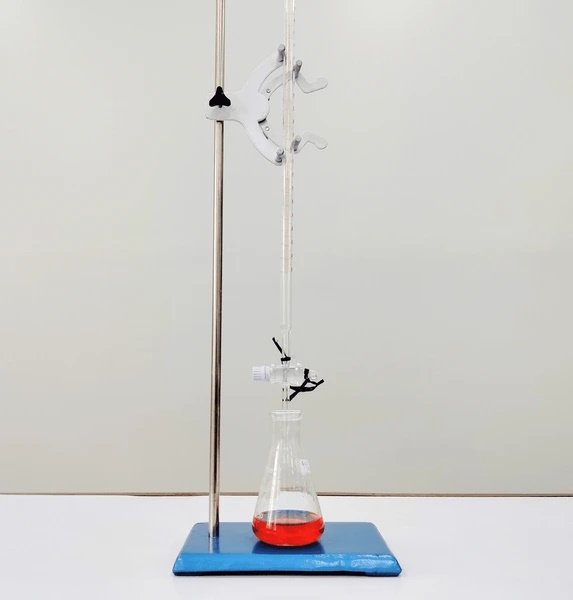

One of the widely accepted instruments to perform titration is the glass burette.
Class A: These are high-precision burettes made from the borosilicate glass, designed to deliver a known volume of a liquid with high accuracy. Often used in analytical chemistry where precision is critical and come with a calibration certificate.
Class B: These are similar to Class A burettes but with a slightly lower accuracy and precision. Class B burettes are suitable for general laboratory work where the precision is not required. They are also made from borosilicate glass and are less expensive than Class A burettes.
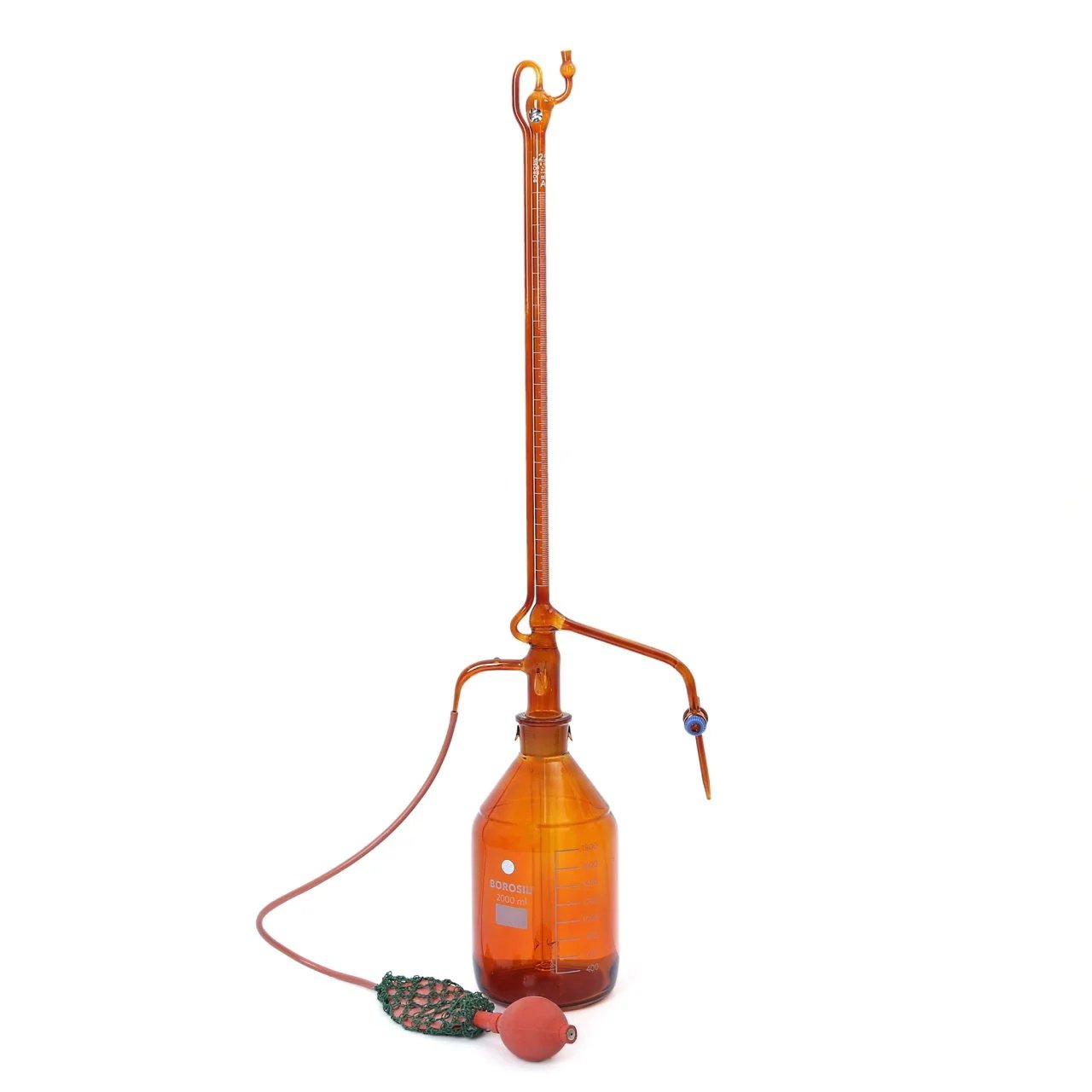
These burettes are designed for continuous titration and equipped with a reservoir bottle that automatically refills the burette.They help in reducing the manual effort and time involved in refilling. Automatic burettes are also available in amber color to protect light-sensitive chemicals. Accurate measurements help minimize errors arising from arithmetic calculations.


Collaborate with Borox to buy high quality burettes, and other laboratory glassware ensuring access to reliable and durable products.
